- Data Visualization Cheat Sheet
- Pandas Cheat Sheet
- Pandas Cheat Sheet Pdf
- Pandas Dataframe Cheat Sheet
- Pandas Visualization Cheat Sheet Free
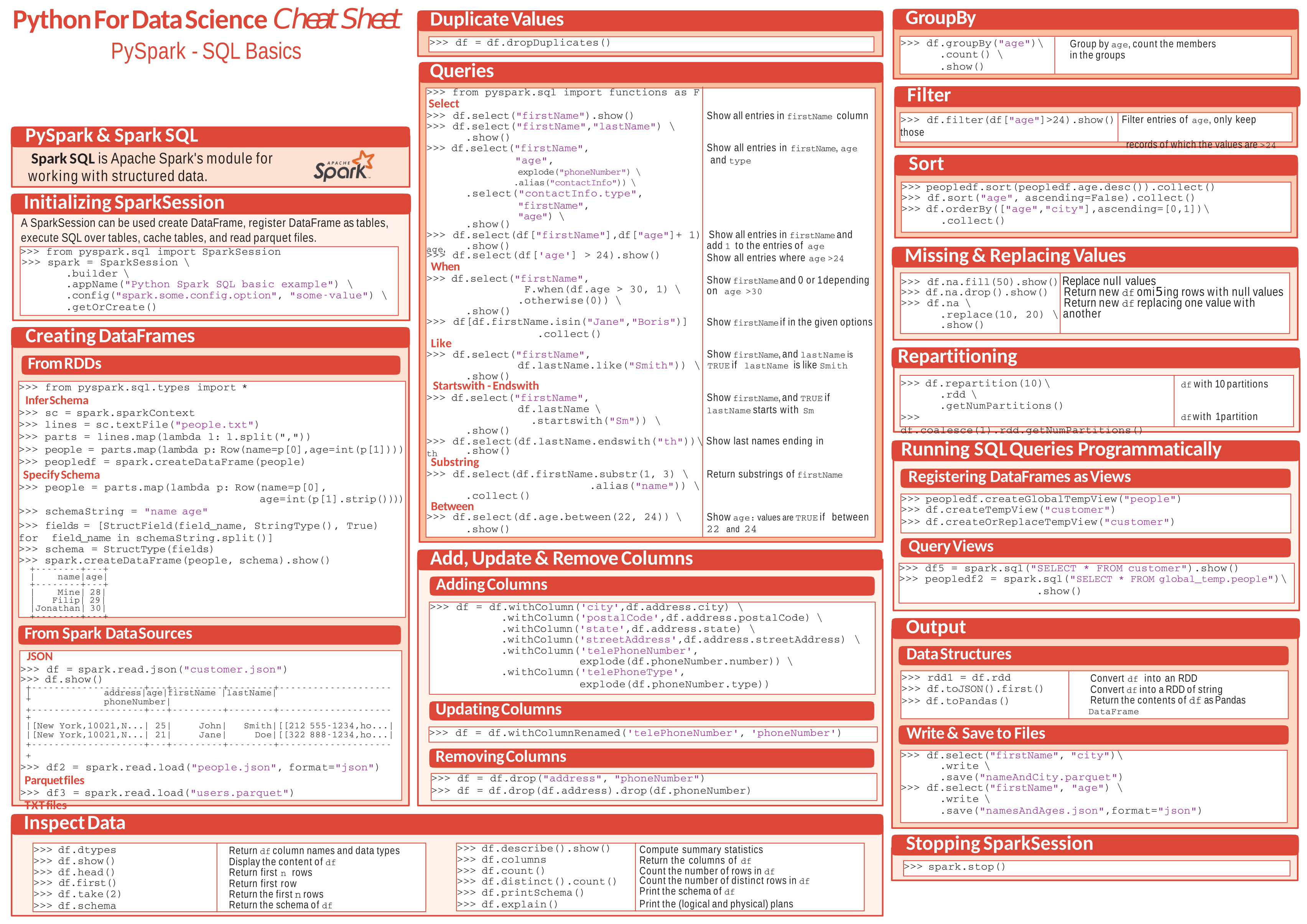
Productivity with Pandas; Pandas data visualization. Pandas allows sql like control on the dataframes. You can treat each DF as a table. This cheat sheet is for visualization using data frame API in pandas. Pandas, visualization, seaborn, matplotlib. Also, seaborn library have advanced visualization functions that are more expressive and are able to express more information more effectively. A little bit of back g round. If you are new to data visualization in python or need a refresher on Matplotlib, please have a look at this article. You can perform data visualization in Pandas as well.
BAR_PLOT_UNIVARIATE_PANDAS
pandas.dataframe.plot.bar(x = optional)LINE_PLOT_UNIVARIATE_PANDAS
pandas.dataframe.plot.line(x = optional)AREA_PLOT_UNIVARIATE_PANDAS
pandas.dataframe.plot.area(x = optional)HIST_PLOT_UNIVARIATE_PANDAS
pandas.dataframe.plot.hist(x = optional)SCATTER_PLOT_BIVARIATE_PANDAS
pandas.dataframe.plot.scatter(x = col_name1, y = col_name2)HEXBIN_PLOT_BIVARIATE_PANDAS
pandas.dataframe.plot.hexbin(x = col_name1, y = col_name2, gridszize = a_number)STACKED_BAR_BIVARIATE_PLOT_PANDAS
pandas.dataframe.plot.bar(stacked = True)LINE_PLOT_BIVARIATE_PANDAS
pandas.dataframe.plot.line(x = optional, y = [])STYLING_PLOT_MATPLOTLIB
pandas.dataframe.plot.bar(figsize = (width, height),color = 'color',
fontsize = ',
title = 'title')
REMOVE_AXIS_SEABORN
sns.despine(bottom = True/False, left = True/False)SUBPLOT_MATPLOTLIB
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize = ())
pandas.dataframe.plot,bar(ax = ax[0])
pandas.dataframe.plot.bar(ax = ax[1])
LOG_PLOT
seaborn.distplot(np.log())SURFACE3D_PLOT_MATPLOTLIB
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
 surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)
surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z)MAP_PLOT
Data Visualization Cheat Sheet
import foliummap = folium.Map(location = [lat,long], zoomstart, tiles = Stamen Toner)
MAP2_PLOT
import foliumPandas Cheat Sheet
map_1 = folium.Map(location = [lat, long], zoom_start = 3.2, tiles = 'Stamen Terrain')LINE_REG_PLOT_SEABORN
seaborn.kdeplot(data:1d array-like)DISTPLOT_SEABORN
seaborn.distplot(data, bins, kde = True/False)JOINTPLOT_SEABORN
seaborn.jointplot(data, x, y)BOXPLOT_SEABORN
seaborn.boxplot(x, y, data)VIOLIN_BOX_PLOT
seaborn.violinplot(x, y, data)FACET_GRID_SEABORN
g = seaborn.FacetGrid(data, row, col)g.map(sns.kdeplot, x)
PAIR_PLOT_SEABORN
seaborn.pairplot(data)LMPLOT_SEABORN
seaborn.lmplot(x, y, hue, data)HEATMAP_SEABORN
seaborn.heatmap(data)Data can be messy: it often comes from various sources, doesn’t have structure or contains errors and missing fields. Working with data requires to clean, refine and filter the dataset before making use of it.
Pandas is one of the most popular tools to perform such data transformations. It is an open source library for Python offering a simple way to aggregate, filter and analyze data. The library is often used together with Jupyter notebooks to empower data exploration in various research and data visualization projects.
Pandas introduces the concept of a DataFrame – a table-like data structure similar to a spreadsheet. You can import data in a data frame, join frames together, filter rows and columns and export the results in various file formats. Here is a pandas cheat sheet of the most common data operations:
Getting Started
Import Pandas & Numpy
Get the first 5 rows in a dataframe:
Get the last 5 rows in a dataframe:
Import Data
Create DataFrame from dictionary:
Import data from a CSV file:
Import data from an Excel Spreadsheet:
Import data from an Excel Spreadsheet without the header:
Export Data
Export as an Excel Spreadsheet:
Export to a CSV file: Drivers h3g usb hsdpa modem.
Convert Data Types
Convert column data to string:
Convert column data to integer (nan values are set to -1):
Convert column data to numeric type:
Get / Set Values
Get the value of a column on a row with index idx:
Set column value on a given row:
Count
Number of rows in a DataFrame:
Count rows where column is equal to a value:
Count unique values in a column:
Count rows based on a value:
Filter Data
Filter rows based on a value:
Filter rows based on multiple values:
Filter rows that contain a string:
Filter rows containing some of the strings:
Filter rows where value is in a list:
Filter rows where value is _not_ in a list:
Filter all rows that have valid values (not null):
Sort Data
Sort rows by value:
Sort Columns By Name:
Rename columns
Rename particular columns:
Rename all columns:
Make all columns lowercase:
Drop data
Drop column named col
Drop all rows with null index:
Drop rows that have missing values in some columns:
Drop duplicate rows:
Create columns
Create a new column based on row data:
Create a new column based on another column:
Create multiple new columns based on row data:
Match id to label:
Data Joins
Join data frames by columns:
Concatenate two data frames (one after the other):
Utilities


Pandas Cheat Sheet Pdf
Drivers etas usb remote ndis network device. Increase the number of table rows & columns shown:
Pandas Dataframe Cheat Sheet
Learn More
Pandas Visualization Cheat Sheet Free
We are covering data analysis and visualization in our upcoming course “Data & the City”. The course will discuss how to collect, store and visualize urban data in a useful way. Subscribe bellow and we’ll notify you when the course becomes available.
