GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Aquarius std s20 s63 driver. They circle the Earth in a geosynchronous orbit, which means they orbit the equatorial plane of the Earth at a speed matching the Earth's rotation. This allows them to hover continuously over one position on the surface. Download md-1 diagnostics interface (com5) driver. The geosynchronous plane is about 35,800 km (22,300 miles) above the Earth, high enough to allow the satellites a full-disc view of the Earth.


Geostationary Means
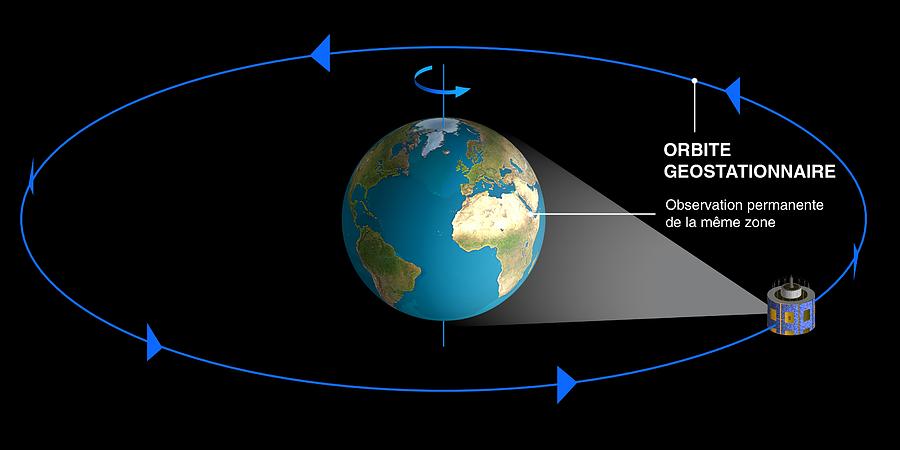
Geostationary definition, of or relating to a satellite traveling in an orbit 22,300 miles (35,900 km) above the earth's equator: at this altitude, the satellite's period of rotation, 24 hours, matches the earth's and the satellite always remains in the same spot over the earth: geostationary orbit. GOES Satellite Network GOES' geostationary status (in which the satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth) allows it to hover over one position on the Earth's surface and provide constant vigil for the atmospheric 'triggers' for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. A geostationary orbit is a path given to high Earth orbiting satellites to monitor weather and for observational and telecommunication purposes. High Earth orbits are orbits that are around 22,236 miles (35,786 kilometers) directly above Earth's equator. Geostationary orbit is that particular orbit where the orbital period of a satellite is equal to that of earth (24 hrs). Due to this, the position of earth and satellite is always fixed. The satellite is always present over a particular region on. One disadvantage of geostationary orbits is the great distance to the Earth, which reduces the achievable spatial resolution. Meteosat and other satellites in geostationary orbit There are a number of weather satellites evenly distributed in geostationary orbit all around the world to provide a global view.
Geostationary Satellite Server
Acer usb modem driver download for windows. Because GOES satellites stay above a fixed spot on the surface, they provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric 'triggers' for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms, and hurricanes. When these conditions develop the GOES satellites are able to monitor storm development and track their movements. GOES satellite imagery is also used to estimate rainfall during the thunderstorms and hurricanes for flash flood warnings, as well as estimates snowfall accumulations and overall extent of snow cover.
Geostationary Vs Geosynchronous
Geostationary Weather Satellites
Geostationary Definition
Such data help meteorologists issue winter storm warnings and spring snow melt advisories. Satellite sensors also detect ice fields and map the movements of sea and lake ice.
